Key Performance Indicators in Manufacturing

What Are Manufacturing KPIs?
Manufacturing KPIs, or Key Performance Indicators, are measurements and metrics that support and facilitate achieving critical goals of the organization. KPIs are very important for understanding and improving manufacturing performance; both from the lean manufacturing perspective of eliminating waste and from the corporate perspective of achieving strategic goals.
Every company measures itself to some degree. Often, these measurements are based on historical information. While there is certainly value in historical analysis, it is a fundamental principle of Key Performance Indicators to be current or forward looking metrics. It is also critical that KPIs be closely aligned to strategic company goals and implemented in such a way as to support positive change.
KPIs for Manufacturing Performance
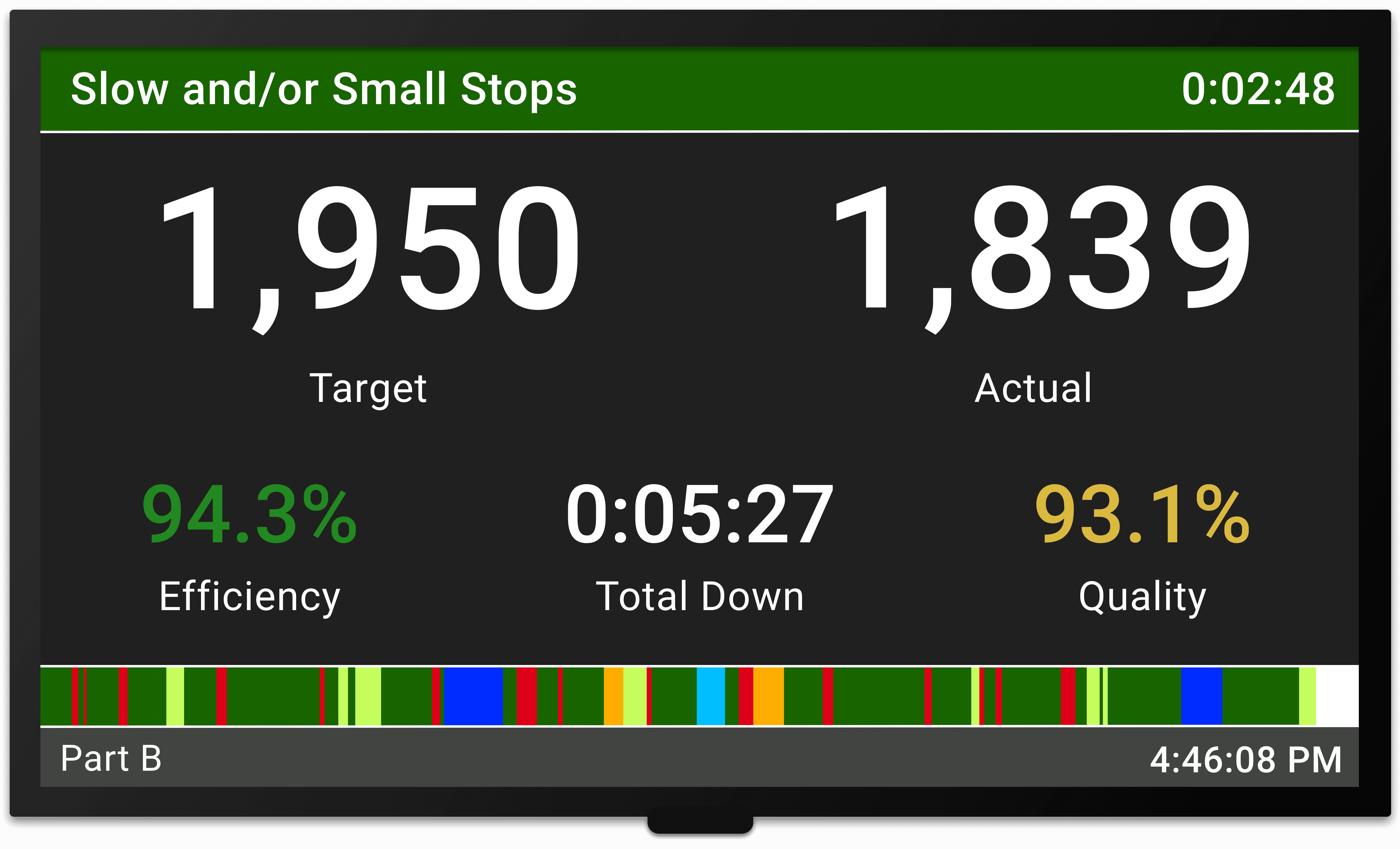
Key Performance Indicators can be highly effective for exposing, quantifying and visualizing muda (the lean term for waste). The essence of lean manufacturing and the central theme of the Toyota Production System (TPS) is to eliminate waste – in other words, to relentlessly eliminate all activities that do not add value for the customer. Effective manufacturing KPIs quantify waste, provide an early warning system for processes operating outside the norm, and offer important hints as to where improvement efforts should be focused.
Key Performance Indicators are also highly effective motivators. Motivation theory (i.e. organizational behavior) is a complex field with many diverse opinions; however, there is wide agreement that a central key to effective motivation is setting challenging but attainable goals (e.g. SMART goals, which are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-Specific). SMART goals are excellent candidates for KPIs.
Effective KPIs can energize the plant floor – unleashing competitive spirit and promoting kaizen (the lean term for continuous improvement). How is this achieved? By providing both a “will” (a strong desire for improvement) and a “way” (effective tools). The “will” flows from a culture of trust. The goal isn't simply to improve a number; it is to truly improve manufacturing performance. Achieving this requires genuine buy-in from the plant floor. The “way” flows from KPIs that can be influenced and controlled by plant floor personnel. After all, if operators can't influence the KPI what value does it provide for them? Collectively, this “will” and “way” create information democracy; empowering plant floor personnel with actionable information and a meaningful level of control over the process.
KPIs must also provide meaningful, reliable, and accurate information. Thus, it is important to carefully define and document the methodology of measurement before implementing a given KPI. Goals and desires are often vague, whereas Key Performance Indicators are meant to be very specific. And, since KPIs are indicators of progress and performance, it is vital that everyone that uses them be able to trust in their accuracy.
An effective way to select a KPI is to first define the behaviors you want to drive, and then select the KPI that best quantifies these behaviors. It is important to avoid unintended consequences that can occur when working to achieve a KPI goal. For example, in manufacturing, a strong focus on top-line OEE can actually drive undesirable behaviors, such as building excessive inventory. It is important to monitor the overall manufacturing process so that any unplanned consequences can be detected and mitigated.
For each goal it is best to have one primary KPI and, optionally, a small number of secondary or supporting KPIs. Otherwise, there is the danger of “information overload.” This is a case where “less is more.” Pick your KPIs like friends - few and well-chosen.
Toyota Production System and KPIs
Lean manufacturing is all about eliminating waste, but “waste” can be a vague and subjective term. The Toyota Production System (TPS) remedies this by defining waste as anything the end customer does not want to pay for. If you are having trouble matching KPIs to your continuous improvement goals, one way to align your KPIs is to understand your largest sources of value and waste. Choose KPIs to measure your largest sources of value and largest sources of waste, and monitor them to ensure your actions eliminate waste while maintaining or increasing value.
For example, an important type of waste in TPS is defective parts. An excellent KPI to measure this form of waste is First Pass Yield, as this metric is aligned to the measurement of OEE Quality. This is also a great example of unintended consequences. It is very common to see an emphasis on Average Rate as a KPI to cause a line to speed up, and you guessed it - create a lower First Pass Yield.
Benefits of Manufacturing KPIs
Can you imagine driving your car without a speedometer or gas gauge? Driving solely based on your rear-view mirror? This is exactly the situation that exists on most plant floors today. Employees often go about their daily tasks and routines with no benchmark to gauge how they are doing, no targets to meet, and not a lot of motivation to improve.
Well chosen KPIs enable managers and operators to keep their fingers on the pulse of the plant floor. They transform subjective debate into objective decisions. Leverage KPIs to make data-driven decisions that leave everyone in your company feeling confident.
5 Steps for Effective Manufacturing KPIs
Here are five steps to creating and maintaining effective KPIs for your manufacturing performance:
- Study the strategic goals of your company.
- Carefully select, define, and document KPIs that will drive the desired behavior.
- Create the “will” and the “way” as described above (e.g. educate, train, and listen).
- Begin using the KPIs to drive improved performance.
- Do it again. Lean is a continuous improvement process. That means your KPIs should evolve as needed to best match the current strategic goals of the company.